General Information about Pristiq
As with most drugs, Pristiq may have some side effects. The mostly reported side effects embrace nausea, dizziness, dry mouth, and constipation. These unwanted facet effects are often gentle and tend to subside with continued use. However, if they persist or turn out to be bothersome, it is essential to consult with a well being care provider.
Pristiq, also recognized by its generic name desvenlafaxine, is a medication primarily used to treat main depressive dysfunction (MDD). It belongs to a class of medication called serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), which work by rising the degrees of those two neurotransmitters within the brain.
In addition to treating despair, Pristiq has also been permitted to treat another mental well being situation called generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). GAD is characterised by excessive and uncontrollable fear and anxiousness about varied features of life, similar to work, relationships, and health. Pristiq is thought to work equally in treating GAD by regulating the degrees of serotonin and norepinephrine within the mind, though it's unclear precisely how it affects this situation.
Once ingested, Pristiq works by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine within the brain. In easier terms, it helps to maintain these chemical substances available for longer durations, thus improving the communication between nerve cells in the brain. This leads to a change in mood and behavior, leading to a discount in symptoms of depression.
Pristiq is prescribed to patients affected by MDD to alleviate these signs and enhance their total high quality of life. While melancholy can be caused by quite lots of elements, together with genetic, environmental, and chemical imbalances in the mind, SNRIs like Pristiq goal the imbalance of neurotransmitters within the brain which might be thought to contribute to the development of despair.
While Pristiq is an effective remedy for melancholy and GAD, it's essential to note that it should not be stopped abruptly. Suddenly stopping the medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms corresponding to headache, nausea, and anxiety. It's important to consult with a physician earlier than discontinuing the usage of Pristiq to avoid these effects.
MDD, commonly known as depression, is a standard mental sickness that affects over 264 million individuals worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. It is characterized by persistent emotions of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in actions that were once loved. Other symptoms might embody modifications in appetite and sleep patterns, problem concentrating, and even suicidal ideas.
In conclusion, Pristiq is a broadly prescribed treatment for the treatment of major depressive dysfunction and generalized anxiousness disorder. It works by inhibiting the reuptake of neurotransmitters in the mind, leading to an improvement in mood and behavior. While it might have some unwanted facet effects, it has proven to be an effective remedy possibility for despair and nervousness when used as directed. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, it is essential to seek help from a healthcare skilled to determine if Pristiq is the proper treatment option.
Let's take a extra in-depth have a look at the medicine itself and the method it works to improve the signs of depression. Pristiq comes in tablet kind and is typically taken as soon as a day, either with or without food. The dosage might range based mostly on an individual's specific wants, and it is necessary to comply with the instructions of a physician rigorously.
The continuous pull-through technique requires the catheter to be withdrawn at a continuous speed from the anal canal symptoms diabetes discount 50 mg pristiq amex, which can provide a detailed recording of pressure profiles, and computer-based three-dimensional representations of the anal canal. With the widespread availability and ease of use of endoanal ultrasound, station pull-through has become more common, with anal canal pressure measurements performed at 1 cm increments in the anal canal. This method provides a more accurate assessment of anal pressures since there is a stabilization period between each reading, thereby reducing artefact. This is the method that the authors perform, with the catheter tip placed 5 cm cephalad from the anal verge. Anal pressure measurements are then taken at 1 cm intervals after a stabilization period of 1020 seconds. Rest and squeeze pressure are recorded at each centimetre up to 1 cm from the anal verge. This test is often useful in patients who are otherwise well, but suffer with chronic constipation refractory to medical management. The test allows a clinician to differentiate between normal transit and slow transit constipation. If more than 20% of the markers remain in an equally scattered fashion, then slow transit constipation exists. If the markers are confined to a particular area of the colon, this may imply some form of obstruction at that point, which needs further investigation. Faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence is the involuntary or inappropriate passage of flatus, liquid or solid stool that is a crucial and hygienic problem. Similarly to urinary incontinence, this can be stress, urge or mixed incontinence. The pathological basis of faecal incontinence can be muscular, neurogenic or idiopathic. Patients may have a decrease in sensory acuity in the anal canal at the anal margins. Often the patient cannot distinguish between the presence of flatus or faeces in the anorectum. This prevents the normal sampling reflex from working appropriately, resulting in, initially, involuntary loss of flatus and liquid stool, progressing to incontinence of formed stool. Faecal incontinence is often underestimated because of the embarrassment and reluctance of patients to discuss this condition. The social stigma and embarrassment of being incontinent of faeces can lead people to severely limit their activity. This rate may be higher in women, especially in those with obstetric-related structural sphincter damage. With increasing age, prevalence of faecal incontinence also rises, which may reflect degenerative changes of the sphincter mechanism over time. Loss of selfesteem, difficulty travelling or maintaining employment, and strain on personal relationships may adversely affect patients and their families, with economic consequences borne by individual and state. Functional manifestations of pelvic floor disease Pelvic floor disease can manifest in a number of ways. This can comprise both functional and anatomical pathology, resulting in disorders of urinary function, faecal function and pelvic organ position. Varying studies have been performed to provide a better understanding of the coexistence of urinary, faecal and genital symptoms. In patients seen with faecal incontinence, 2055% also complained of urinary incontinence, with 720% also complaining of genital prolapse. Conversely, of patients presenting with rectal prolapse, over 60% also complained of urinary disturbance and 30% of genital prolapse. The frequent coexistence of urinary and colorectal dysfunction indicates the need for a multidisciplinary approach to the evaluation of patients with these conditions. Pathophysiology of faecal incontinence Normal defecation and continence require a complex interplay of several important factors. The rectum, which functions as the organ of storage, requires appropriate distensibility, compliance and sensory ability. The passive musculature which maintains continence should be of sufficient calibre and contractility, providing an adequate resting pressure to hold back stool in the rectum. The voluntary muscles should also be of normal length and thickness and contract appropriately, maintaining an acute anorectal angle, so that the faecal bolus is supported over the levator muscle and not directly over the anal canal. The outflow system should be intact, and stool transit time should also be within normal range. Denervation has been found in the pelvic floor muscles of patients with constipation and defecation disorders that cause excessive straining. In patients with abnormal descent of 23 cm, a stretching force to the distal nerve of 2030% is therefore exerted. Stretching of these nerves during straining may lead to secondary neuropathic damage with consequent pudendal neuropathy. Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine that occurs during physical activity such as coughing, sneezing, laughing or exercise. It is a distressing problem of bladder storage in which the strength of the urethral sphincter is diminished and unable to prevent urine flow when there is increased abdominal pressure. This is often, but not exclusively, the result of weakness of pelvic floor support with resulting rotational descent of the bladder neck and proximal urethra during increases in intraabdominal pressure.
The tendency of a solution to hold water or "pull" water into it is called osmotic pressure 3 medications that affect urinary elimination discount generic pristiq canada. Osmotic pressure is directly related to the concentration of solutes in the solution. The higher the solute concentration, the greater the osmotic pressure and the greater the tendency of water to move into the solution. Many molecules, particularly proteins and some ions, are prevented from diffusing through the plasma membrane. Consequently, any change in their concentration on one side of the membrane forces water to move from one side of the membrane to the other, causing cells to lose or gain water. The ability of a solution to change the size and shape of cells by altering the amount of water they contain is called tonicity (ton-isi-te; ton = strength). As you might guess, interstitial fluid and most intravenous solutions are isotonic solutions. If red blood cells are exposed to a hypertonic (hiper-tonik) solution-a solution that contains more solutes, or dissolved substances, than there are inside the cells-the cells will begin to shrink. This is because water is in higher concentration inside the cell than outside, so it follows its concentration gradient and leaves the cell (photo b). Hypertonic solutions are sometimes given to patients who have edema (swelling of the feet and hands due to fluid retention). Such solutions draw water out of the tissue spaces into the bloodstream so that the kidneys can eliminate excess fluid. When a solution contains fewer solutes (and therefore more water) than the cell does, it is said to be hypotonic (hipo-tonik) to the cell. Cells placed in hypotonic solutions plump up rapidly as water rushes into them (photo c). Because it contains no solutes at all, water will enter cells until they finally burst, or lyse. Hypotonic solutions are sometimes infused intravenously (slowly and with care) to rehydrate the tissues of extremely dehydrated patients. Each is smaller and has less cytoplasm than the mother cell, but it is genetically identical to it. The daughter cells grow and carry out normal cell activities until it is their turn to divide. Mitosis and division of the cytoplasm usually go hand in hand, but in some cases the cytoplasm is not divided. This condition leads to the formation of binucleate (two nuclei) or multinucleate cells. As mentioned earlier, mitosis provides the "new" cells for body growth in youth and is necessary to repair body tissue all through life. Transcription the word transcription often refers to one of the jobs done by a secretary-converting notes from one form (shorthand notes or an audio recording) into another form (a letter, for example). In other words, the same information is transformed from one form or format to another. Fibrous (structural) proteins are the major building materials for cells (see Chapter 2). Other proteins, the globular (functional) proteins, do things other than build structures. For example, all enzymes, biological catalysts that regulate chemical reactions in the cells, are functional proteins. Just as different arrangements of notes on sheet music are played as different melodies, variations in the arrangements of A, C, T, and G in each gene allow cells to make all the different kinds of proteins needed. Translation A translator takes words in one language and restates them in another language. In the translation phase of protein synthesis, the language of nucleic acids (base sequence) is "translated" into the language of proteins (amino acid sequence). They1 can do this because they have a special three-base se2 quence called an anticodon on their "head" that can bind to the complementary codons (3). Recall that the joining of amino acids by enzymes into peptide bonds is the result of 6 dehydration synthesis reactions (Chapter 2, p. What are the two stages of protein synthesis, and in which stage are proteins actually synthesized When the last codon (the termination, or "stop," codon) is read, 6 the protein is released. The human body, complex as it is, starts out as a single cell, the fertilized egg, which divides almost endlessly. Some become muscle cells, others the transparent lens of the eye, still others skin cells, and so on. Thus, there is a division of labor in the body, with certain groups of highly specialized cells performing functions that benefit the organism as a whole. When a small group of cells is indispensable, its loss can disable or even destroy the body. For example, the action of the heart depends on a very specialized cell group in the heart muscle that controls its contractions. If those particular cells are damaged or stop functioning, the heart will no longer work efficiently, and the whole body will suffer or die from lack of oxygen. The four primary tissue types-epithelium, connective tissue, nervous tissue, and muscle-interweave to form the fabric of the body. If we had to assign a single term to each primary tissue type that would best describe its overall role, the terms would most likely be covering (epithelium), support (connective), movement (muscle), and control (nervous). However, these terms reflect only a tiny fraction of the functions that each of these tissues performs. Tissues are organized into organs such as the heart, kidneys, and lungs (see Chapter 1).
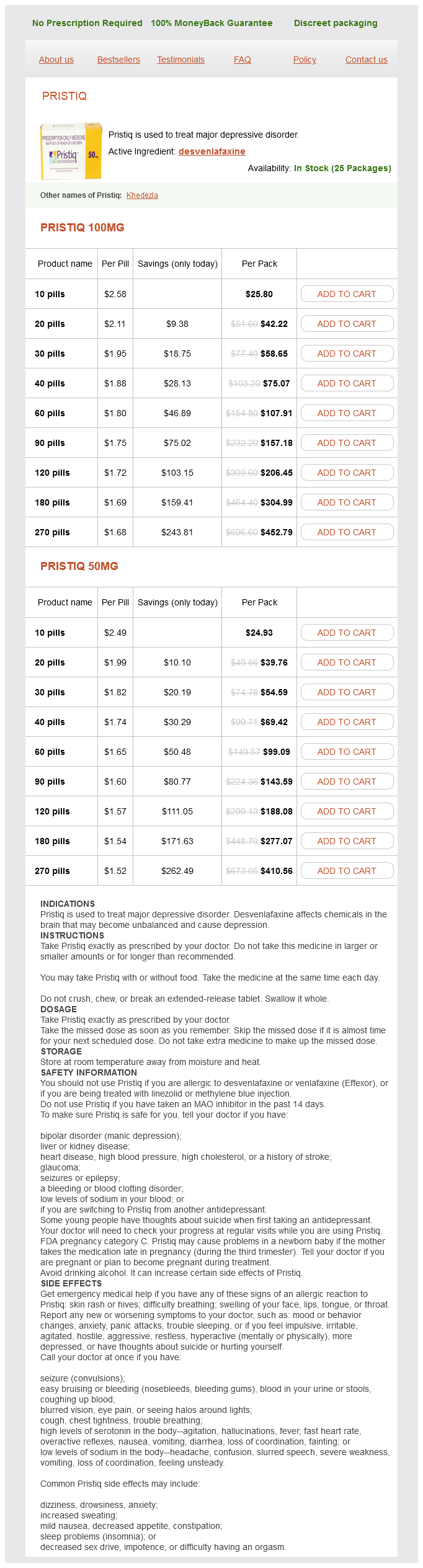
Pristiq Dosage and Price
Pristiq 100mg
- 10 pills - $25.80
- 20 pills - $42.22
- 30 pills - $58.65
- 40 pills - $75.07
- 60 pills - $107.91
- 90 pills - $157.18
- 120 pills - $206.45
- 180 pills - $304.99
- 270 pills - $452.79
Pristiq 50mg
- 10 pills - $24.93
- 20 pills - $39.76
- 30 pills - $54.59
- 40 pills - $69.42
- 60 pills - $99.09
- 90 pills - $143.59
- 120 pills - $188.08
- 180 pills - $277.07
- 270 pills - $410.56
However treatment centers discount pristiq 100 mg, herniation also may result when the vertebral column is subjected to exceptional twisting forces. If the protruding disc presses on the spinal cord or the spinal nerves exiting from the cord, numbness and excruciating pain can result. The discs and the S-shaped structure of the vertebral column work together to prevent shock to the head when we walk or run. The spinal curvatures in the thoracic and sacral regions are referred to as primary curvatures because they are present when we are born. In adults, the secondary curvatures allow us to center our body weight on our lower limbs with minimum effort. The cervical curvature appears when a baby begins to raise its head, and the lumbar curvature develops when the baby begins to walk. These abnormalities may be congenital (present at birth) or result from disease, poor posture, or unequal muscle pull on the spine. As you look at these photos, try to pinpoint how each of these conditions differs from the normal healthy spine. The common features of vertebrae include the following: · Body or centrum: disclike, weight-bearing part of the vertebra facing anteriorly in the vertebral column. In addition to these common features, vertebrae in the different regions of the spine have very specific structural characteristics. Cervical Vertebrae the seven cervical vertebrae (identified as C1 to C7) form the neck region of the spine. The first two vertebrae (atlas and axis) are different because they perform functions not shared by the other cervical vertebrae. The superior surfaces of its transverse processes contain large depressions that receive the occipital condyles of the skull. They are larger than the cervical vertebrae and are distinguished by the fact that they are the only vertebrae to articulate with the ribs. The two transverse processes of each thoracic vertebra articulate with the nearby knoblike tubercles of the ribs. Lumbar Vertebrae the five lumbar vertebrae (L1 to L5) have massive, blocklike bodies. Because most of the stress on the vertebral column occurs in the lumbar region, these are the sturdiest of the vertebrae. The winglike alae articulate laterally with the hip bones, forming the sacroiliac joints. Its posterior midline surface is roughened by the median sacral crest, the fused spinous processes of the sacral vertebrae. The vertebral canal continues inside the sacrum as the sacral canal and terminates in a large inferior opening called the sacral hiatus. It is the human "tailbone," a remnant of the tail that other vertebrate animals have. They are the smallest, lightest vertebrae, and most often their spinous processes are short and divided into two branches. The transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae contain foramina (openings) through which the vertebral arteries pass on their way to the brain above. Any time you see these foramina in a vertebra, you should know immediately that it is a cervical vertebra. Explore human cadaver >Study Area> bones around the organs of the thoracic cavity (heart, lungs, and major blood vessels). Sternum the sternum (breastbone) is a typical flat bone and the result of the fusion of three bones- the manubrium (mah-nubre-um), body, and xiphoid (zifoid) process. The sternum has three important bony landmarks-the jugular notch, the sternal angle, and the xiphisternal joint. It provides a handy reference point for counting ribs to locate the second intercostal space for listening to certain heart valves. Because the sternum is so close to the body surface, it is easy to obtain samples from it of blood-forming (hematopoietic) tissue for the diagnosis of suspected blood diseases. A needle is inserted into the marrow of the sternum, and the sample is withdrawn; this procedure is called a sternal puncture. Because the heart lies immediately posterior to the sternum, the physician must 158 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology take extreme care not to penetrate the sternum during this procedure. The true ribs, the first seven pairs, attach directly to the sternum by costal cartilages. False ribs, the next five pairs, either attach indirectly to the sternum or are not attached to the sternum at all. The last two pairs of false ribs lack the sternal attachments, so they are also called floating ribs. The intercostal spaces (spaces between the ribs) are filled with the intercostal muscles, which aid in breathing. Besides the ribs and sternum, there is a third group of bones forming the thoracic cage. The clavicle acts as a brace to hold the arm away from the top of the thorax and helps prevent shoulder dislocation. When the clavicle is broken, the whole shoulder region caves in medially, which shows how important its bracing function is. The scapulae (skapu-le), or shoulder blades, are triangular and are commonly called "wings" because they flare when we move our arms posteriorly.
© 2025 Adrive Pharma, All Rights Reserved..